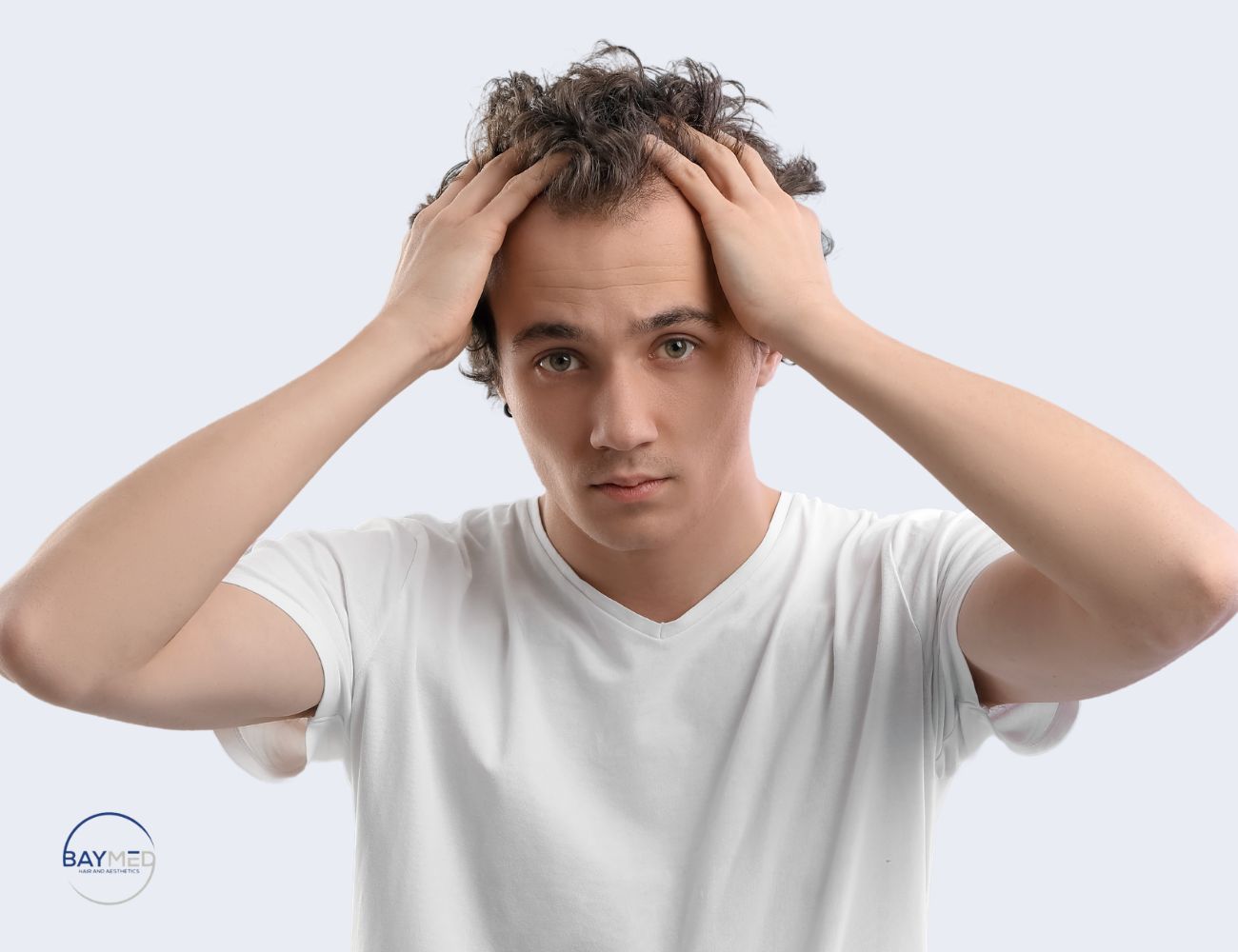
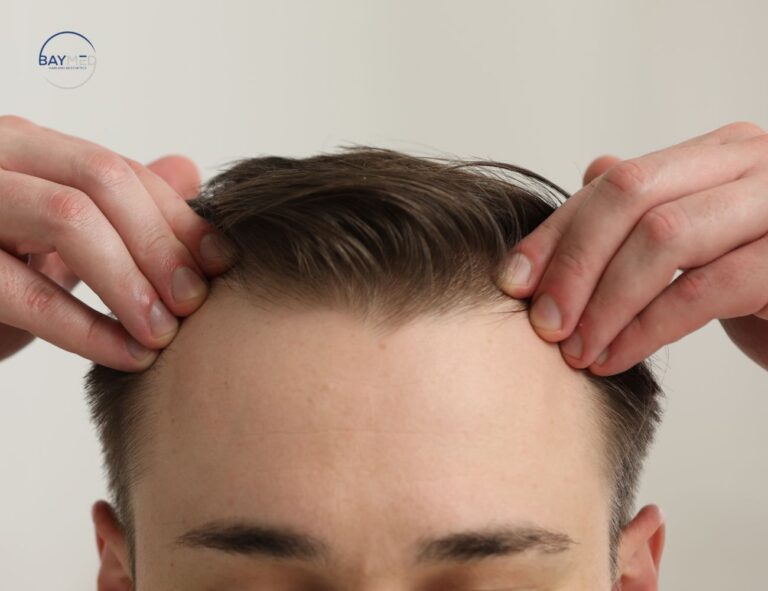
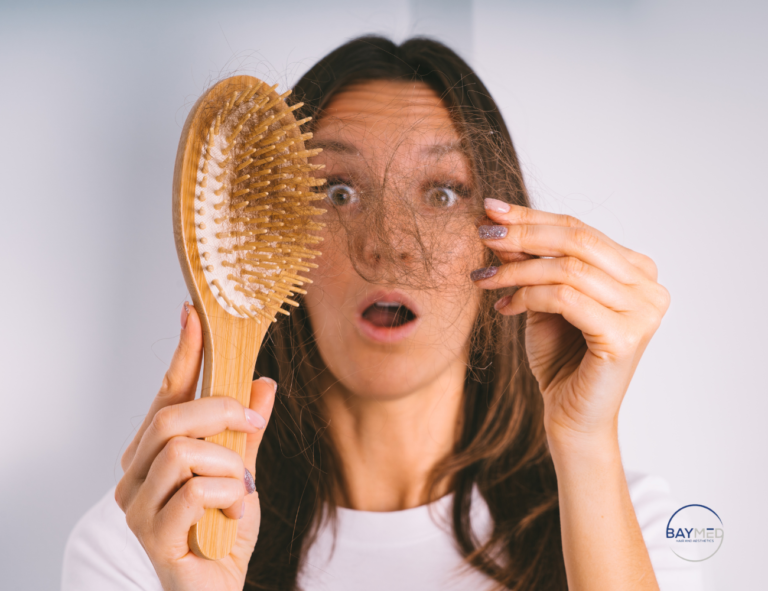
Hair loss can be a challenging experience, but modern hair restoration techniques offer effective solutions for regaining confidence and achieving natural-looking results. Two of the most popular methods are Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). While both techniques are effective in treating hair loss, FUE has become the preferred choice for many due to its advanced technology, minimal invasiveness, and superior results. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key differences in FUE vs. FUT, emphasizing why FUE is often considered the better option for hair restoration.
Table of Contents
What Are FUE and FUT?
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a minimally invasive hair transplant technique in which individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area (typically the back or sides of the head) using a micro-punch tool or robotic assistance. These harvested follicles are then meticulously transplanted into the recipient area, addressing regions of thinning or balding.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also called the strip hair restoration method, involves removing a thin strip of tissue from the donor area. Individual hair follicles are then carefully dissected from this strip under a microscope and transplanted into the recipient area.
Key Differences Between FUE and FUT
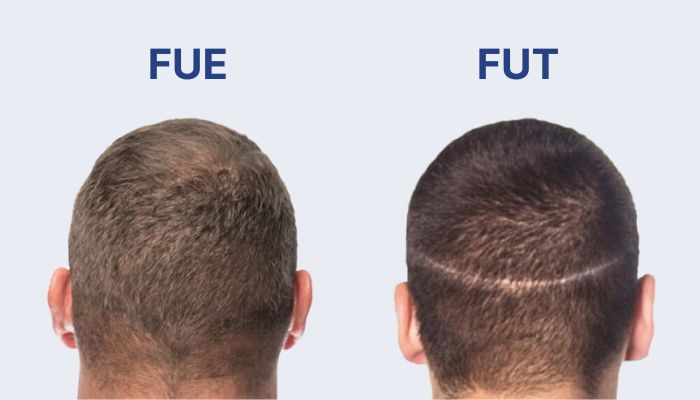
Extraction Method
The fundamental difference between FUE and FUT lies in the method of hair follicle extraction. In Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), individual hair follicles are extracted one at a time from the donor area. This method is minimally invasive, as it doesn’t require cutting or stitching. Each follicle is carefully extracted, reducing the risk of damage to the hair follicles and surrounding tissues.
In contrast, Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, typically from the back of the scalp. This strip is then dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope before being transplanted into the recipient area. FUT is a more invasive method due to the need for a surgical incision and dissection of the skin.
Scarring
One of the most notable differences between FUE and FUT lies in the type of scarring each procedure leaves behind.
FUE is renowned for its ability to extract individual follicles using a micro-punch tool or robotic assistance. This method leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are virtually invisible to the naked eye, even with short hairstyles. The distributed nature of the extraction ensures a natural appearance in the donor area, making FUE the ideal choice for those who prefer short hair or want to minimize visible scarring.
In contrast, FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, which results in a linear scar. While the scar can often be concealed with longer hairstyles, it remains a limitation for those who wish to wear their hair short. Over time, this linear scar can also widen or become more noticeable, especially if additional FUT procedures are performed.
Recovery Time
FUE offers a significantly shorter recovery period compared to FUT, thanks to its minimally invasive approach. Most FUE patients experience only mild discomfort and can return to normal activities within a few days. The absence of stitches or large incisions further contributes to the swift healing process, allowing patients to resume their routines with minimal disruption.
FUT, on the other hand, typically requires a longer recovery period due to the size of the incision and the need for sutures. Patients may experience tightness, discomfort, and swelling in the donor area, often requiring several weeks to fully recover. This longer downtime can be a significant drawback for individuals with busy schedules or those seeking a quick return to normalcy.
Donor Area Quality
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) offers more flexibility by allowing the surgeon to harvest follicles from multiple areas of the scalp. This is especially useful for patients with limited donor hair density, as it helps maintain the fullness of the donor region and minimizes thinning. By extracting hair from different sites, FUE ensures a more even distribution and can achieve a natural result, even in cases of diffuse thinning.
In contrast, FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) is best suited for patients with dense donor hair. Since FUT involves removing a strip of scalp, it relies on a concentrated area of healthy follicles. This method works well for those with ample donor hair but may cause thinning if the donor area is sparse or not dense enough.
Summary
Both FUE and FUT are effective hair restoration methods, but FUE stands out as the superior option for most patients. Its minimally invasive nature, faster recovery, and natural results make it a popular choice among individuals seeking to restore their hair and confidence.
If you’re considering hair restoration, consult with a qualified hair transplant specialist to determine the best approach for your unique needs.