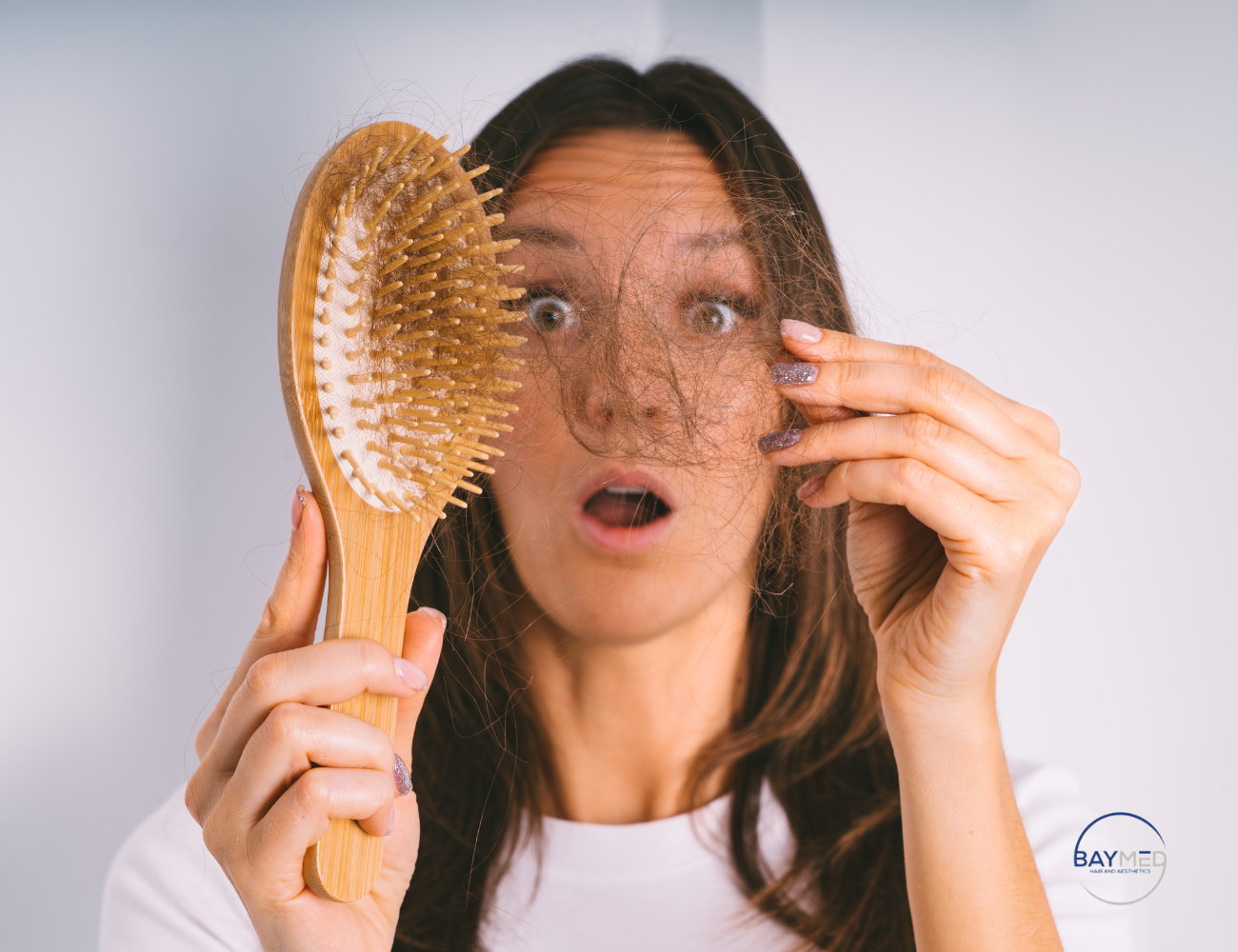
Welcome to motherhood! Alongside the joys of bonding with your new baby, you may be noticing some changes—particularly in your hair. If you’ve noticed hair shedding several months post-birth, you’re not alone. Known as post-partum hair loss, this common condition affects many new mothers. But what causes it, and how can you manage it? Let’s dive into everything you need to know.
Table of Contents
What is Post-Partum Hair Loss?
Post-partum hair loss, also known as “post-partum shedding,” is the hair loss that many women experience after giving birth. While it might feel like you’re “losing hair,” it’s actually the body’s way of returning to its normal hair growth cycle. During pregnancy, hormonal changes encourage more hair follicles to stay in the growing (anagen) phase, leading to thicker hair. However, as hormones stabilize after birth, these follicles enter the shedding (telogen) phase simultaneously, causing noticeable hair loss. This process is usually temporary, lasting from a few months to a year.
Causes of Post-Partum Hair Loss
Understanding why post-partum hair loss happens can help in both managing expectations and knowing that it’s part of a natural process.
- Hormonal Shifts: After childbirth, estrogen levels drop, affecting hair’s growth phase. As a result, hair that stayed put for months now begins to fall out.
- Physical Stress and Recovery: Childbirth is physically demanding. The recovery process requires energy that the body redirects, sometimes resulting in hair shedding.
- Lack of Sleep and Increased Stress: Caring for a newborn is exhausting, and lack of sleep or increased stress can exacerbate hair loss by disrupting hair’s growth cycle.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Many nutrients, including iron, vitamin D, and B vitamins, are crucial for healthy hair growth. New mothers, especially those breastfeeding, may find themselves deficient if they’re not getting adequate nutrition.

Managing and Minimizing Post-Partum Hair Loss
There is no way to entirely prevent post-partum hair loss, but there are ways to manage and potentially minimize it.
Nutritional Support
- Increase Protein Intake: Hair is primarily made of protein. Ensure you’re getting enough through lean meats, fish, and plant-based options.
- Vitamins and Supplements: Nutrients like Biotin, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Iron, and Omega-3 fatty acids are essential. Consider a post-natal multivitamin.
- Stay Hydrated: Hair needs moisture, and so does your body—especially if you’re breastfeeding. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
Be Gentle with Your Hair
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Braids, buns, and ponytails pull on the hair and can worsen shedding.
- Limit Heat and Chemical Exposure: Excessive heat styling or harsh chemicals can damage hair, making it more prone to breakage.
- Use Wide-Tooth Combs and Soft Brushes: This helps reduce tangling and breakage, especially with wet hair.
Optimize Hair Care Routine
- Choose Gentle, Nourishing Products: Look for sulfate-free shampoos, gentle conditioners, and hair masks designed for hydration and strengthening.
- Regular Scalp Massages: Scalp massages increase blood circulation to hair follicles and can stimulate hair growth. You can use natural oils like coconut or castor oil to gently massage the scalp. Castor oil is known for its high concentration of ricinoleic acid, which promotes scalp health, while coconut oil can strengthen and protect the hair shaft.
Managing Stress Levels
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, and gentle yoga can help reduce stress.
- Seek Support: Joining a new mothers’ group or talking to a counselor can help you manage the stress of new motherhood.

Realistic Expectations and When to Seek Professional Help
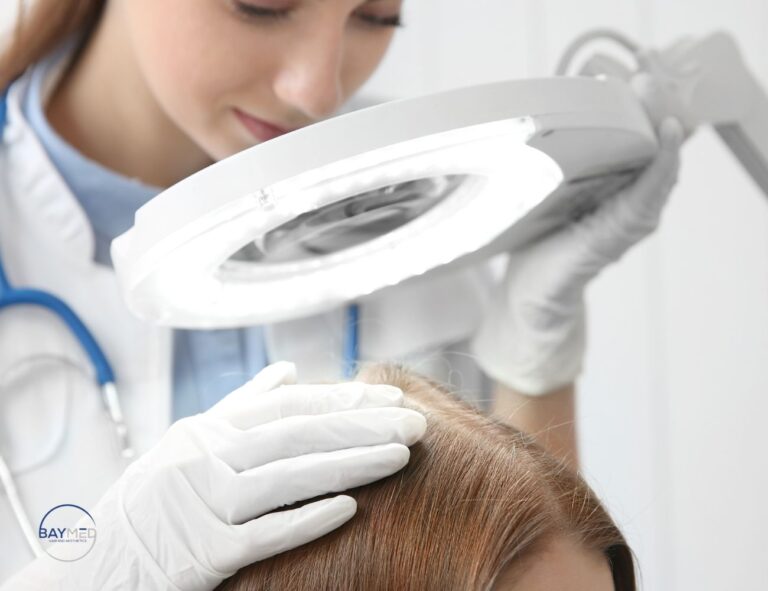
Post-partum hair loss can be distressing, but remember it’s a temporary condition that usually resolves within a year. However, if you notice patchy hair loss or if your hair doesn’t seem to be regrowing, it may be time to seek advice from a dermatologist.
When to See a Dermatologist
- Severe Shedding or Bald Spots: If you’re experiencing bald spots, it could be a sign of alopecia or another underlying condition.
- No Improvement After a Year: For many women, hair growth normalizes within a year. If yours hasn’t, a professional can suggest treatments or run tests for any hormonal or nutritional deficiencies.
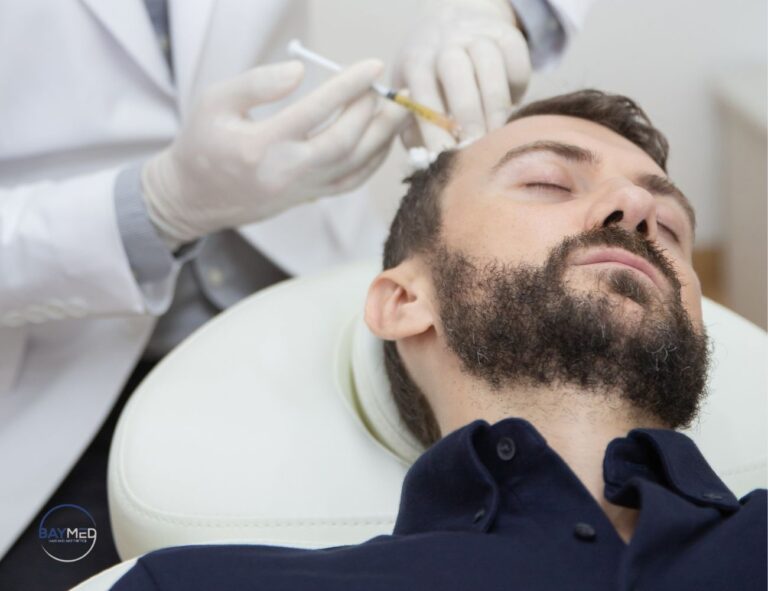
- If You’re Interested in Scalp Treatments: Treatments like PRP, or Mesotherapy should only be administered by licensed professionals.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy
PRP therapy involves using a patient’s own blood to stimulate hair regrowth. Here’s how it works and its potential benefits for post-partum hair loss:
- How PRP Works: In PRP therapy, a small amount of your blood is drawn, then processed to separate the platelet-rich plasma, which is packed with growth factors. This concentrated plasma is injected into the scalp where hair thinning or shedding is prominent, stimulating the hair follicles.
- Benefits for Post-Partum Hair Loss: The growth factors in PRP can help repair damaged hair follicles and increase blood circulation in the scalp, supporting the return of healthy hair growth. For many women experiencing post-partum hair shedding, PRP can expedite the hair restoration process, especially if hair growth has been slow to return to its normal cycle.
- Safety Considerations: Because PRP uses your own blood, it’s generally safe, with minimal risk of an allergic reaction. However, it’s crucial to work with a licensed practitioner, especially if you’re breastfeeding, to ensure treatment suitability.
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy involves injecting small amounts of vitamins, amino acids, and other active ingredients directly into the scalp. Here’s what makes it effective and how it may support post-partum hair health:
- How Mesotherapy Works: A cocktail of nutrients and vitamins tailored to stimulate hair growth is injected into the scalp at a shallow depth, near the hair follicles. These nutrients help boost circulation, reduce inflammation, and provide the follicles with the support they need for healthy growth.
- Benefits for Post-Partum Hair Loss: Post-partum hormonal shifts and nutrient deficiencies can weaken hair roots and slow regrowth. Mesotherapy can help counteract this by directly nourishing the scalp and promoting a healthy environment for hair regrowth. It’s particularly beneficial for replenishing lost nutrients, often critical in post-partum cases.
- Safety Considerations: Mesotherapy is generally safe and minimally invasive; however, it is not recommended for women who are breastfeeding. To ensure the health and safety of both mother and child, it is typically advised to wait until breastfeeding is complete before pursuing mesotherapy for hair restoration.
Summary
Post-partum hair loss is a common experience for many new mothers, but it’s temporary and manageable. By understanding the process and implementing healthy lifestyle choices, you can navigate this phase more confidently. Remember that hair shedding after childbirth is a natural part of your body’s adjustment, and over time, with a little patience and care, your hair will regain its fullness. Embrace this transition, prioritize self-care, and celebrate the incredible journey of motherhood.